Introduction
A slow or not functioning network can be frustrating if you are at home, in a workplace, or if you own a business. As a Computer System Technician student at St. Lawrence College, I have gained experience in network troubleshooting using software such as Cisco Packet Tracer. In this blog, I will elaborate on simple steps to troubleshoot, most important tools, and actual examples of fixing everyday network problems from my studies using Cisco Packet Tracer.
What is Network Troubleshooting?
Network troubleshooting refers to the activity of detecting and fixing problems that make devices incapable of connecting to the internet or to each other. The issue could be as simple as a loose cable or as complex as a router with a misconfigured setting. The secret is to approach the process step by step to detect and fix the problem efficiently.
Common Network Problems and Real-Life Examples
These are some of the common reasons why networks fail and some examples from my Cisco Packet Tracer lab exercises on how to fix them:
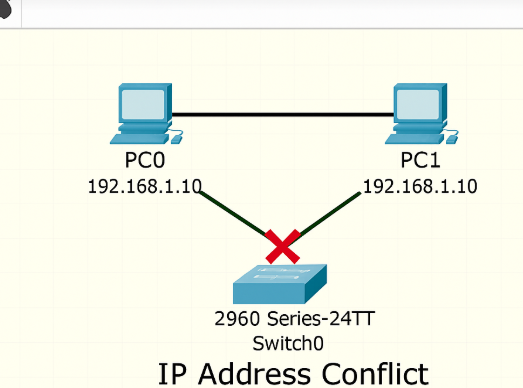
IP Address Conflicts – Two computers within the same network having the same IP address, thus not being able to communicate well.
Example: I was trying to complete a Cisco Packet Tracer exercise when I built a network with some PCs, but the machines would not connect. While troubleshooting, I realized I had assigned a wrong static IP to two of the machines. Changing one of the IP addresses resolved the issue immediately.
DNS Issues – Websiteseven will fail to load when the Domain Name System (DNS) is incorrect.
Example: I was performing a Cisco Packet Tracer simulation where I was configuring a home office network. Some computers were not accessing websites, though they were connected to the internet. I checked the settings and found that they were configured to use an incorrect DNS server. Changing to Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8) resolved the issue.
Slow Internet Speed – Slow speed is caused by congestion in the network, weak Wi-Fi signals, or old hardware.
Example: While running a sample office network inside Cisco Packet Tracer, we tested different settings to see how much would make the network run slow. What we discovered is that one 100 Mbps switch had too heavy traffic. Our performance improved substantially after we went with a gigabit switch and deployed VLANs.
Router Configuration Issues – Incorrect configuration of a router can create connectivity issues for a network.
Example: While setting up a network on Cisco Packet Tracer, I realized that certain devices were unable to access the internet. Upon checking the router settings, I realized that the default gateway was set incorrectly. Fixing the default gateway fixed the issue and allowed all devices to connect as needed.
Firewall Blocking Connections – Firewalls are designed to protect, but incorrect settings can block traffic needed.
Example: While working on a task of configuring the firewall on Cisco Packet Tracer, I accidentally blocked all traffic entering instead of restricting external threats only. Local devices were not able to communicate as a result. Changing the firewall settings to allow internal connections while maintaining security solved the problem.
Useful Tools in Troubleshooting
IT administrators employ various tools to diagnose and fix network problems:
Ping – Checks whether a device is online and receiving.
Tracert (Windows) / Traceroute (Linux/Mac) – Shows the path data takes to reach a destination.
IPConfig (Windows) / IfConfig (Linux/Mac) – Show network settings.
NSLookup – Helps find LAN problems.
Wireshark – Network traffic sniffer and identifying suspicious activity.
Netstat – Shows open connections and connection status.
Easy Steps to Fix Network Issues
Define the Issue – Have users describe what is wrong and what isn’t working.
Check Cables and Connections – Make sure everything is plugged in correctly.
Verify IP Settings – Execute ipconfig or ifconfig to confirm network settings.
Test Network Connection – Ping to confirm devices can talk to each other.
Check Router and Firewall Settings – Make sure they are not blocking internet access.
Analyze Network Traffic – Employ Wireshark to watch data flow and detect problems.
Restart Devices – Rebooting the computer, router, or modem may resolve problems.
Get Help if Needed – If the problem continues, get help from a network technician or internet service provider.
A Real Situation from My Experience
During one of my Cisco Packet Tracer network labs, I needed to set up and troubleshoot a network. Initially, some computers were unable to communicate with the router. With the utilization of ping and traceroute, I discovered that the router’s interface had not been assigned an IP address. After assigning the correct IP and subnet mask, the entire network functioned correctly. I learned the importance of checking configurations step by step instead of assuming the issue is hardware-related.
Conclusion
It is an important skill for IT technicians to understand how to troubleshoot network issues. With knowledge of typical issues, the right equipment, and simple step-by-step troubleshooting procedures, any one can diagnose and fix network issues fast. My experiences with Cisco Packet Tracer taught me these skills, which will be helpful for me in future IT careers.
Leave a Reply